The GRC buyer’s guide for 2025: Building resilience with AI-powered, federated solutions
For organizations managing various entities, business units, or clients, the challenge of ensuring compliance and effective security implementation across complex regulatory requirements, distributed operations, and varying service needs necessitates a unique solution. Our GRC buyer's guide dissects the federated GRC model and dives into the benefits of centralized control and localized autonomy for government, aerospace and defense, advisors and managed service providers, banking and financial institutions, manufacturing, and more. Discover the capability you should expect from a modern GRC platform, including turn-key, full-stack cyber GRC capabilities, continuous compliance, and advanced, AI-powered solutions that go beyond basic automation. Learn why 6clicks is the solution for your GRC program. Download now!
-1.png?width=200&height=249&name=Group%20193%20(1)-1.png)
The expert's guide to The GRC buyer’s guide for 2025: Building resilience with AI-powered, federated solutions
-1.png?width=314&height=391&name=Group%20193%20(1)-1.png)
Contents
What is Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC)?
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a term that has become increasingly common in recent years. GRC refers to the management of an organization's overall strategy and approach to governance, risk management, and compliance with industry regulations and external requirements, to ensure they support and enable the organization's strategic objectives.
What are the key elements of an effective GRC program?
An effective GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) program consists of several key elements that work together to ensure the organization's adherence to regulations, risk management, and to maintain a strong ethical and compliant culture.
Let's explore each of these elements in detail:
-
Governance: Governance is the foundation of a robust GRC program. It involves establishing a clear organizational structure, defining roles and responsibilities, and implementing effective decision-making processes. Strong governance ensures that the organization's objectives and strategies align with its overall mission and values. It also includes establishing oversight mechanisms such as committees and board structures to monitor and guide GRC efforts.
-
Risk management: Effective risk management is crucial for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could hinder the achievement of organizational goals. This involves implementing risk assessment processes, assigning risk owners, developing risk mitigation strategies, and regularly monitoring and reviewing risk exposure. A comprehensive understanding of the types of risks across your risk landscape enables proactive decision-making and promotes operational resilience in the face of uncertainties. Most risk management programs focus on either enterprise risk management, operational risk management or compliance risk management.
-
Compliance processes: Compliance processes encompass the development and implementation of policies, procedures, and controls to ensure adherence to applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies. This element involves assessing compliance requirements, establishing control frameworks, conducting regular compliance monitoring, and promptly addressing any compliance breaches. Robust compliance processes foster ethical behavior and protect the organization from legal and reputational risks.
-
Ethics and culture: An organization's ethical values and culture play a critical role in driving responsible behavior and shaping the decision-making process. This element involves establishing a strong ethical framework, promoting ethical awareness and accountability, and fostering a culture of integrity and transparency throughout the organization. An ethical and compliant culture serves as a strong foundation for effective GRC practices and helps in building trust with stakeholders.
-
Information technology: Information technology is an essential component of modern GRC programs. It involves leveraging technology solutions to automate and streamline GRC processes, enhance data collection and analysis, and ensure the security and privacy of sensitive information. Technology enables efficient risk assessments, real-time monitoring, and reporting, facilitating informed decision-making and enabling timely response to emerging risks and compliance issues.
To develop and implement these key elements effectively, organizations can utilize frameworks such as the GRC Capability Model developed by OCEG. This model provides a holistic approach to integrating governance, risk management, compliance, ethics/culture, and IT into a unified GRC program. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the organizational context, aligning strategies and objectives, performing actions to promote desirable outcomes and detect incidents, and continuously reviewing and improving the GRC program.
What you should be looking for in GRC software?
GRC software to address specific use cases
GRC software is designed to provide organizations with a range of capabilities they can use as an automation tool for one or more use cases. Some of the common use cases of GRC software include:
-
Risk management: GRC software solutions enable organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. They provide risk assessment tools that help organizations to evaluate the likelihood and impact of various risks and to develop risk mitigation strategies. Learn more about the 6clicks solution for Enterprise Risk Management (ERM).
-
Compliance management: GRC software solutions provide compliance teams with tools to manage compliance with regulatory and industry standards. These tools automate compliance monitoring and reporting, making it easier for organizations to stay up to date with evolving regulations such as government regulations, privacy regulations, cyber regulations and ESG regulations. Learn more about the 6clicks solution for Regulatory Compliance.
-
Audit management: GRC software solutions provide tools for audit professionals to manage internal and external audits. These tools automate the audit process, making it easier for organizations to prepare for audits and to track audit findings and recommendations. Learn more about the 6clicks solution for Audit & Assessment.
-
Policy management: GRC software solutions provide tools to manage policies and procedures. These tools enable organizations to create, review, approve, and distribute policies and procedures, and to monitor compliance with them.
- Third-party risk management: GRC software solutions provide tools for vendor managers to centralize and simplify the vendor lifecycle by automating third-party vendor discovery, risk assessment, and remediation, freeing up time to strengthen your security posture. Learn more about the 6clicks solution for vendor risk management.
GRC software features
Governance, Risk and Compliance software solutions are designed to help organizations manage their risk, compliance and governance needs through a range of features and functionalities. Here are some key features of GRC software that business units should look for:
- Artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence within GRC software helps risk and compliance professionals automate a range of manual and time-consuming tasks such as compliance mapping between standards, laws and regulations, control set mapping back to compliance obligations to help identify areas of compliance and non-compliance, documentation of controls and automated vendor risk assessment responses. The scope and application of actionable intelligence within GRC software is immense with generative AI, machine learning, predictive models and document generation. Explore the 6clicks Hailey AI engine.
- Content and document management: Content and document management is a crucial component of GRC software solutions. It allows organizations to create, track, store and manage content related to their compliance and risk management processes. This includes policies, procedures, guidelines, and other critical documents. A GRC software solution should offer an easy-to-use interface to create, edit, manage, and share documents with key stakeholders.
- Risk management and analytics: Risk management and analytics is another key feature of GRC software. This feature allows organizations to identify, quantify, and assess risks across the enterprise. GRC software should provide an automated risk management process, from identification to analysis, to prioritization, and mitigation. With robust reporting and analytics capabilities, organizations can generate real-time dashboards and risk reports, track progress, and make data-driven decisions.
- Workflow management: Workflow management is an essential component of GRC software. It helps organizations to establish, execute, and monitor GRC-related critical workflows such as compliance and risk assessments, policy management, and issue management. It allows users to create workflows, assign tasks to relevant stakeholders, and track progress in real-time. Workflow management helps organizations ensure that tasks are completed on time, efficiently, and effectively.
- Audit management: GRC software should simplify the internal audit process. Audit management is a critical feature of GRC software that helps organizations conduct audits, assess findings, and implement corrective actions. Audit management should provide a centralized platform to manage audit plans, schedules, findings, and remediation. Automated workflows can help organizations manage the audit process more efficiently and effectively.
- Predictive analytics, reporting and dashboards: An integrated dashboard and actionable insights are vital features of GRC software. It provides a real-time visibility of key performance indicators relevant to business processes and objectives. A intuitive dashboard allows users to monitor compliance and risk-related activities with real-time insights to make informed decisions. Dynamic dashboards should be customizable and offer visualizations for complete visibility and to provide an easy-to-understand summary of critical data.
Buying GRC software value and considering the alternatives
The traditional types of GRC software vendors
The GRC software market has and remains highly fragmented with hundreds of providers. The good news for buyers, is there are lots of alternatives and plenty of choice. However, it's important to understand the three categories of GRC software vendors in order to make an informed decision.
Legacy software providers
Most of the software that was built 8+ years ago would fall into this category if not one of the others below. The core characteristics are:
- On-premise or single-code base: These providers typically offer on-premise solutions or rely on multiple (or forked) code bases with cloud-based instances globally.
- Complexity: Legacy systems are intricate and often require extensive customization, leading to long deployment times, increased costs, and challenges in adapting to regulatory changes or internal processes.
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist using these complex systems, necessitating extensive training and hindering adoption across the organization.
- High investment, poor ROI: Legacy systems often demand substantial investment with limited return on investment due to their rigid use cases and deployment difficulties.
Industry specialized providers
Examples of software in this category tend to exhibit these characteristics:
- Niche focus: These vendors cater to specific industries, which can benefit organizations within their sector but may lack flexibility outside their specialization.
- Integration challenges: Managing risks and compliance across multiple industries can be complex when integrating different specialized solutions, potentially leading to data silos and inefficiencies.
- Limited scalability: Specialized providers might struggle to adapt their solutions as organizations grow or diversify, potentially requiring additional GRC tools.
Point solutions
By definition, point solutions address a single pain point or use case for customers and tend to exhibit these characteristics:
-
Fragmentation: Point solutions are designed to address specific GRC needs, such as AML/KYC, business continuity management, compliance training or threat intelligence. While they excel in their respective areas, using multiple point solutions can create fragmentation in an organization's GRC landscape. This can make it difficult to have a holistic view of risk and compliance.
-
Integration complexity: Integrating multiple point solutions can be complex and costly. Organizations may need to invest in middleware or custom development to ensure these solutions work together seamlessly.
-
Lack of comprehensive reporting: Point solutions often provide robust reporting within their specific domain but may lack the ability to generate comprehensive reports that cover all aspects of governance, risk, and compliance. This can make it challenging to provide stakeholders with a unified view of the organization's risk posture.
Although there's been plenty of point solution software on the market, our research points to a marked shift in buyers' preferences away from points solutions given the need to manage a more integrated, complex market.
Challenges with traditional GRC software
The issue with traditional GRC software stems from their limitations in terms of supporting multiple use cases, different context and varied requirements across a diverse organizations needs. This problem The result of this is a sub-optimal return-on-investment (ROI) on two major fronts:
- the number of use cases you can streamline and automate across a complex and distributed business.
- the difficulty in adoption because they are difficult to quickly deploy across even a moderately complex organization.
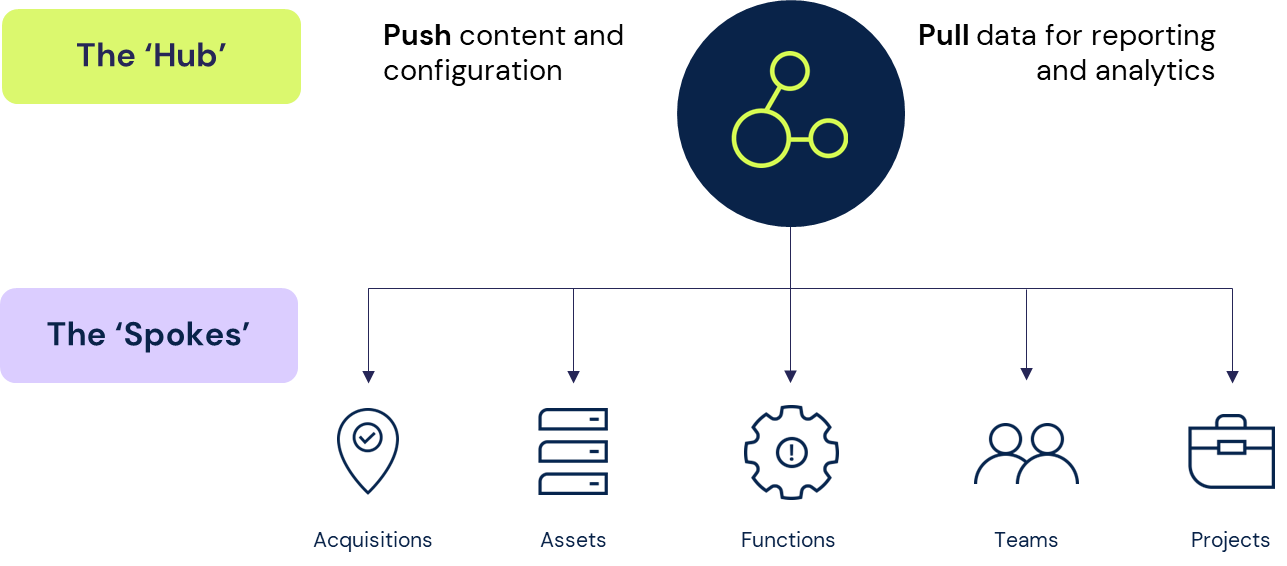
The 6clicks GRC platform is an alternative approach because the platform was built with multi-tenancy at the customer level - not an afterthought. At 6clicks, we call this approach "Hub & Spoke". This revolutionary approach allows businesses to deploy multiple team instances across their organization (spokes) that are all connected to a central account (Hub).
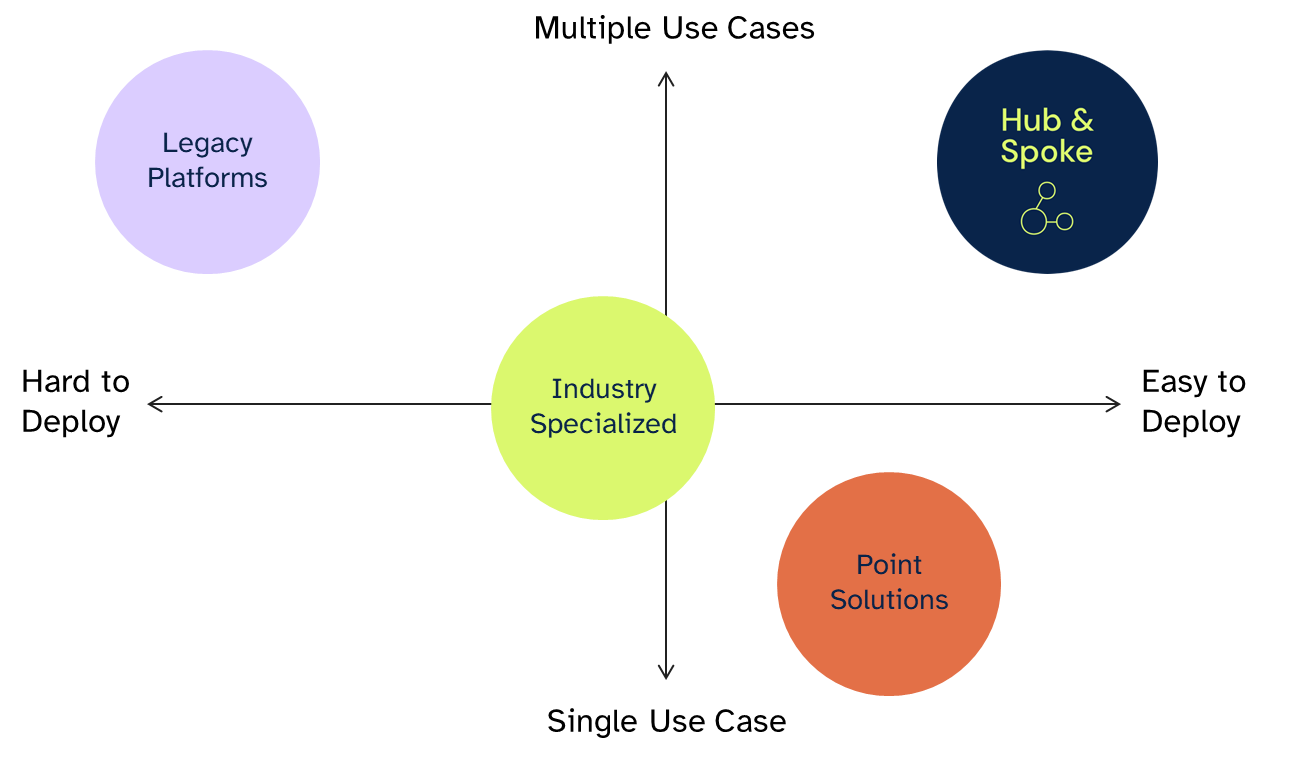
So what is 6clicks Hub & Spoke?
The 6clicks Hub & Spoke is the perfect solution for large businesses, multinationals, franchises, private equity firms, government agencies and MSPs requiring a centralized risk and compliance function that spans multiple teams, departments, or businesses. With the Hub & Spoke model, organizations can quickly and easily define the hierarchical structure that works best for them, which includes parent-child relationships between entities.
The hub makes it possible to define risk and compliance best-practice and content centrally, which is 'pushed down' to spokes (teams, departments, or businesses) that utilize the full suite of 6clicks GRC modules for day-to-day activities. Consolidated reporting and analytics are rolled up at the hub level, giving the organization comprehensive reporting and insights across all spokes.
Traditional GRC software licensing
Traditional Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) software pricing can be based on a variety of parameters, and the pricing models may vary from one vendor to another. Here's a breakdown of some common pricing parameters for traditional GRC software:
-
Per User: Many GRC software vendors charge based on the number of users or seats. Each user who needs access to the GRC platform is counted, and the pricing is typically on a per-user basis. This model is often tiered, with different pricing levels for different user roles or access levels.
-
Per Module: GRC software often consists of multiple modules or components that cater to different aspects of governance, risk management, and compliance. Vendors may offer pricing options based on the specific modules a customer wants to use. Customers can select the modules they need and pay accordingly.
-
Per Content License: Some GRC solutions offer access to specific content libraries, such as regulatory compliance content, templates, or best practices. Pricing can be based on the level of content access or licensing required.
-
Per Vendor: For organizations that need to manage and assess risks related to their vendors or suppliers, GRC software might offer pricing based on the number of vendors or suppliers that are being monitored and managed through the platform.
-
Per Compliance Framework: GRC software often supports multiple compliance frameworks and standards, such as SOC2, ISO, NIST, or industry-specific regulations. Pricing may vary based on the number of compliance frameworks a customer wants to implement or the complexity of the compliance requirements.
It's essential for organizations to carefully evaluate the pricing models offered by GRC software vendors to ensure they align with their budget and requirements. Additionally, organizations should consider factors like scalability, support, training, and ongoing maintenance costs when making their GRC software purchasing decisions.
A better alternative: 6clicks software licensing
With its innovative pricing model, a cost-effective alternative to traditional GRC software is offered by cloud-based software platform 6clicks. Unlike the conventional per-user, per-module, or per-compliance framework pricing structures, 6clicks introduces a game-changing approach. With 6clicks, organizations can enjoy unlimited access to a comprehensive suite of GRC tools and functionalities, encompassing all the elements required for effective governance, risk management, and compliance. What sets 6clicks apart is its simple and transparent "pay-per-spoke" pricing system. This means that organizations pay only for the specific components, or "spokes," they need, tailoring their GRC solution precisely to their requirements. This approach not only maximizes cost efficiency but also ensures that businesses can adapt their GRC capabilities as they evolve, without the constraints of traditional pricing models. It's a modern and adaptable solution that empowers organizations to take full control of their GRC needs while keeping costs in check.
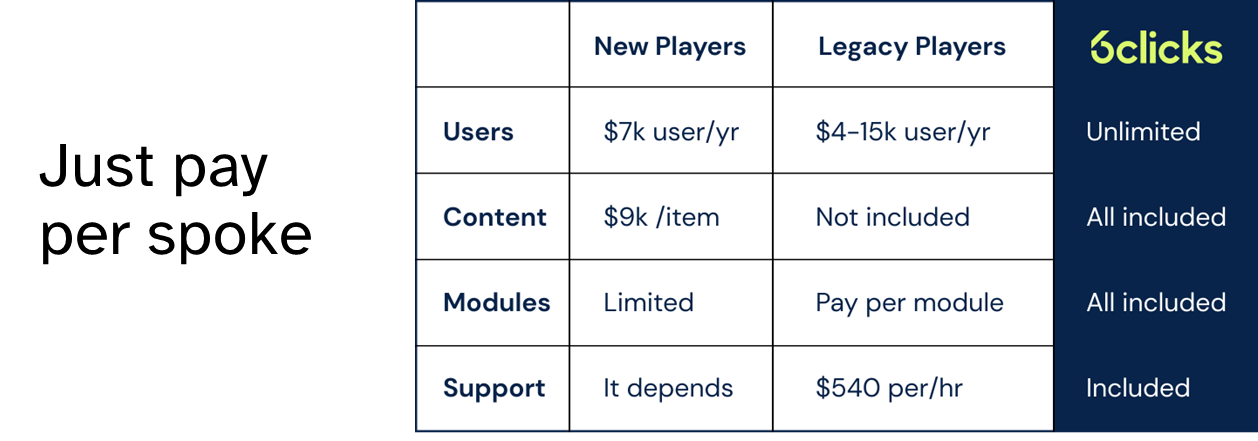
Optimizing your return on investment (ROI) from GRC software
6clicks can significantly improve your return on investment (ROI) by offering a range of benefits that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive value across your governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) efforts:
-
Cost Efficiency: With 6clicks' pay-per-spoke pricing model, you only pay for the specific GRC components you need. This eliminates the need to invest in a one-size-fits-all solution that may include unnecessary features. As a result, your GRC costs are directly aligned with your actual requirements, optimizing your spending and improving cost efficiency.
-
Time Savings: 6clicks provides pre-built templates, assessments, and content libraries, streamlining the GRC process. This saves significant time in risk assessments, compliance audits, and policy management. Your team can focus more on strategic tasks rather than repetitive administrative work, leading to increased productivity.
-
Scalability: 6clicks allows you to scale your GRC solution as your organization grows or your needs change. You can easily add or remove "spokes" as required, ensuring that your GRC capabilities remain aligned with your evolving business demands without incurring additional overhead.
-
Visibility and Reporting: The platform offers real-time visibility into your GRC data, making it easier to track and mitigate risks, monitor compliance, and make data-driven decisions. Improved reporting capabilities enable you to demonstrate compliance more effectively to stakeholders and regulators, potentially reducing compliance fines and penalties.
-
Collaboration: 6clicks promotes collaboration across your organization by providing a centralized platform for GRC activities. Enhanced communication and collaboration lead to better risk identification and mitigation, ultimately protecting your bottom line.
-
Reduced Errors: Automation within 6clicks reduces the risk of human error in GRC processes. This can prevent costly compliance violations, security breaches, and reputational damage, further safeguarding your ROI.
-
Competitive Advantage: By efficiently managing risks and compliance, you gain a competitive edge. Customers and partners are more likely to trust and do business with organizations that demonstrate a strong commitment to governance, risk management, and compliance, ultimately bolstering your revenue.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Staying compliant with industry regulations is crucial. 6clicks helps you maintain compliance more efficiently, reducing the likelihood of fines and penalties associated with non-compliance, which can significantly impact your ROI.
In summary, 6clicks improves your ROI by optimizing costs, saving time, enhancing scalability and flexibility, improving visibility, reducing errors, and ensuring compliance. By empowering your organization to effectively manage GRC processes, 6clicks contributes to both cost savings and revenue protection, ultimately boosting your overall return on investment.
RFI and RFP templates to support your GRC software procurement
6clicks provides a suite of Request for Information (RFI) and Request for Proposal (RFP) templates to assist organizations in streamlining their procurement processes. These templates are designed to simplify the procurement of goods or services, including technology solutions like GRC software.
Implementing GRC software
To implement an effective GRC strategy, organizations can follow these steps:
-
Establish GRC requirements: Understand the organization's exposure and prioritize GRC efforts. Assess existing risk management and compliance activities, consult with executives and management, and compare policies and practices with GRC objectives. Consider sensitive business areas and regulatory requirements to establish long-term goals.
-
Choose the right GRC software: Identify GRC technologies that enhance the organization's business model and address security risks and compliance gaps. Look for a comprehensive solution that meets all GRC requirements, considering automation capabilities and unified data management to avoid complexity.
-
Prepare software for integration: Integrate the selected GRC solution with current policies and processes. Seek consultations and demos from the software provider, assign internal roles and responsibilities for implementing GRC, and define specific steps for software utilization.
-
Develop GRC policies and procedures: Create comprehensive GRC policies and procedures that align with objectives and regulatory requirements. Outline roles, protocols for risk assessment and mitigation, and compliance measures. Communicate these policies and procedures effectively throughout the organization.
-
Provide training and education: Implement a training program to educate employees on GRC concepts, policies, and procedures. Offer specialized training for individuals involved in GRC activities, focusing on risk awareness, ethical behavior, and necessary skills. Evaluate the effectiveness of training initiatives regularly.
-
Establish GRC communication channels: Create open communication channels for reporting risks, compliance violations, and ethical concerns. Encourage feedback and suggestions for improving GRC processes. Implement whistleblower hotlines or anonymous reporting systems to ensure confidentiality and foster accountability.
-
Conduct internal audits and assessments: Regularly conduct internal audits and continous assessments to evaluate GRC effectiveness. Review controls, assess compliance, and identify areas for improvement. Document findings and develop action plans for remediation and enhancement.
-
Keep track of GRC progress: Continuously monitor GRC implementation progress, evaluate performance based on predefined metrics, assess risks, review controls, and update policies. Adapt to changing regulations and industry standards with ongoing focus on risk management and compliance.
-
Foster continuous improvement: Promote a culture of continuous improvement in GRC. Encourage feedback, conduct periodic reviews, stay updated on emerging risks and regulatory changes, and benchmark against industry peers. Embrace best practices to enhance GRC processes.
-
Establish a GRC committee or steering group: Form a dedicated GRC committee or steering group with representatives from various departments and stakeholders. Provide oversight, guidance, and direction for GRC initiatives. Regularly review performance, address challenges, and make strategic decisions to strengthen the overall GRC framework.
Subscribe to receive all the latest updates
Subject to 6clicks Privacy Policy, you agree to allow 6clicks to contact you via the email provided for scheduling and marketing purposes.

